News & Blogs 2024-07-02
Chemiluminescence: The Future of Immunodiagnostics
EN
CN
EN
News & Blogs 2024-07-02
Chemiluminescence: The Future of Immunodiagnostics
Chemiluminescence is widely used in clinical diagnostics, especially in detecting disease markers through specific antigen-antibody reactions. It’s employed in diagnosing infectious diseases, heart diseases, tumors, pregnancy, and more, with over 100 markers in use.

Chemiluminescence Definition and Examples (thoughtco.com)
Compared to other methods, chemiluminescence offers comprehensive advantages in safety, automation, accuracy, and speed, making it the leading trend in immunodiagnostics.
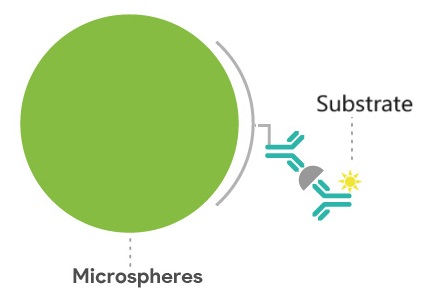
According to the American Clinical Chemistry Conference, any method measuring photon count qualifies as chemiluminescence. Compared to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), chemiluminescence has made significant strides in automation, quantification precision, material use, and antibody labeling techniques.
1. Low Concentration Detection: The substances being measured are in very low concentrations (μg/L to pg/L), requiring extremely high precision in the detection system, including closed instrument and reagent systems.
2. Complex Procedures: The detection process involves many steps, making automation challenging.
3. Interdisciplinary Technologies: It encompasses advanced technologies from biology, chemistry, physics, and optics, each indispensable.
The Principle of Chemiluminescence
● Immune Response: When an antigen enters the body, it triggers an immune response, leading to the production of specific antibodies.
● Immunoassay (IA): Utilizes the specific reaction between known antigens or antibodies and the analyte in body fluids to detect antibodies or antigens.
● High Specificity and Affinity: The antigen-antibody reaction is highly specific and forms a stable complex, essential for immunoassays.
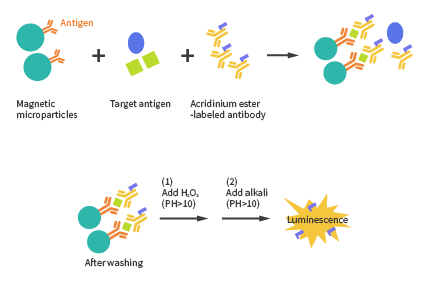
Globally, mainstream reagent technologies include:
● Direct Chemiluminescence: Iso-luminol (New Industries), acridinium ester (Abbott)
● Indirect (Enzyme-Mediated) Chemiluminescence: Danaher, Mindray, Antu
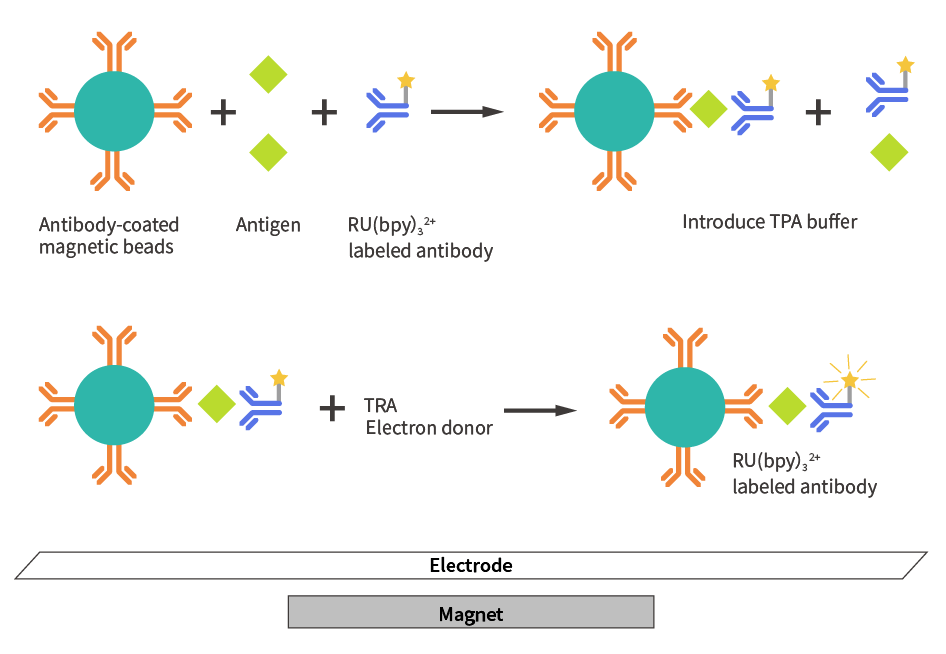
● Electrochemiluminescence: Roche
Each has its pros and cons with no clear trend towards a single dominating technology, although electrochemiluminescence is considered a third-generation technology with slight technical advantages.
Different technologies have their own advantages:
● Acridinium Ester, ALP, and HRP Systems: Each has specific strengths and weaknesses.
● Electrochemiluminescence: Slightly more advanced and recognized in the market.
Key Performance Metrics for Reagents and Instruments
● Reagent Performance: Includes accuracy, sensitivity, linear range, interference resistance, storage stability, open-bottle stability, and kit specifications.
● Instrument Performance: Includes detection speed, reagent positions, sample positions, and instrument size. Accuracy is the core metric, usually compared against certified products, while other performance factors indirectly affect accuracy.
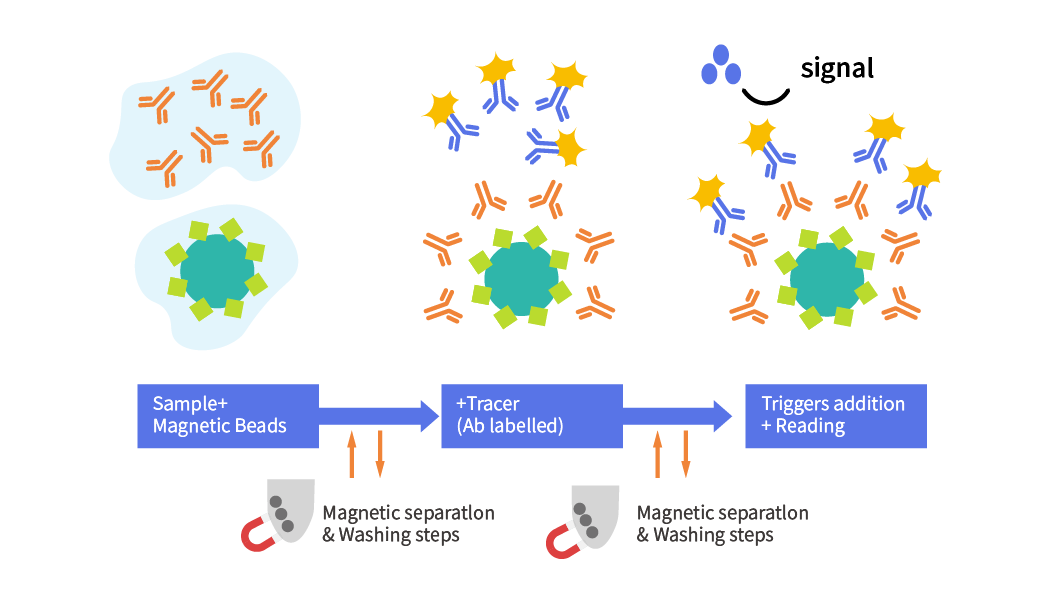
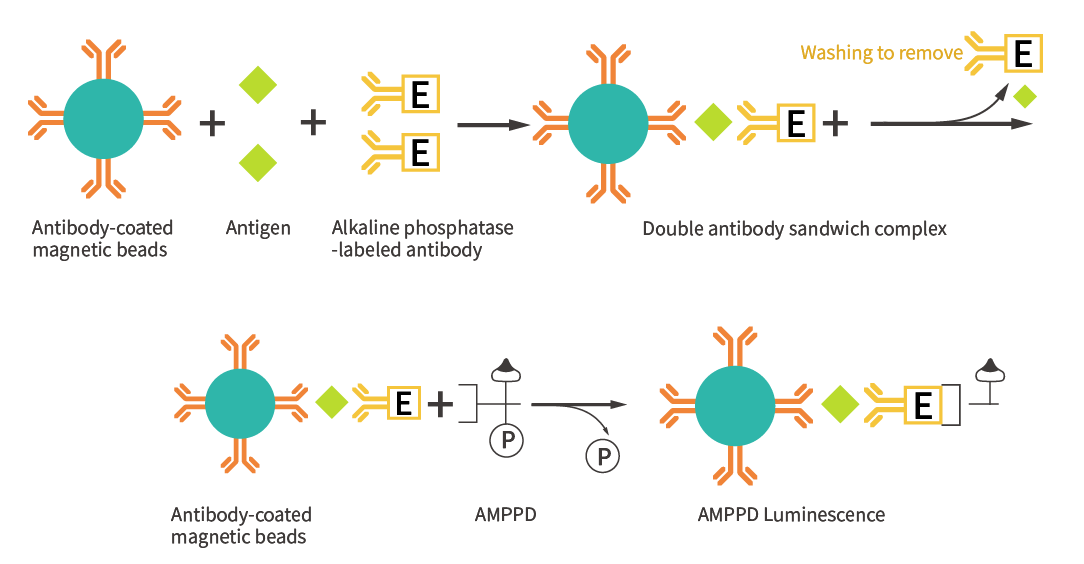
Explanation of the principles of chemiluminescence: an example of an enzymatic method (two-step method)
Schematic diagram of EC immunosensor for multiple mycotoxin detection. Adapted from Lu and Gunasekaran (2019).
Chemiluminescence involves multiple steps:
● One-step, two-step, three-step, and four-step methods depending on the number of washes.
● Requires precise temperature control and handling volumes in the 5-200 µL range.
● Sample analogs can significantly impact results.
Instrument performance is gauged by fault rates, design, speed, and capacity, while reagent performance is judged by accuracy, sensitivity, repeatability, linearity, and stability. Comprehensive evaluations consider installation numbers, usage rates, project counts, and hospital adoption rates.
Chemiluminescence immunoassay stands out as a leading diagnostic technology due to its precision, automation capabilities, and broad clinical applications, making it a vital tool in modern healthcare diagnostics.