News & Blogs 2024-05-22
IVD Materials Empowering Dengue Fever Detection
EN
CN
EN
News & Blogs 2024-05-22
IVD Materials Empowering Dengue Fever Detection
● High Fever: Sudden onset, usually lasting 2-7 days
● Severe Headache: Often pain behind the eyes
● Joint and Muscle Pain: Known as "breakbone fever" due to its severity
● Rash: Appears on the 3rd-5th day, may be maculopapular or petechial
● Nausea and Vomiting
● Fatigue and Weakness
Some patients may develop severe dengue (previously known as dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome), characterized by severe bleeding, plasma leakage, and organ damage, requiring immediate medical intervention.
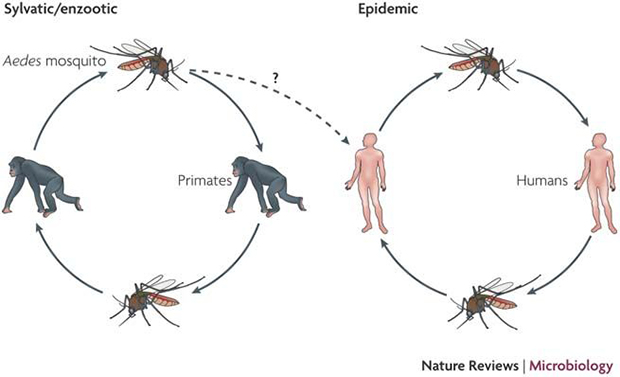
from:Nature Reviews Microbiology
Dengue fever is a critical public health concern due to its widespread prevalence in tropical and subtropical regions and its potential for severe complications. Accurate and timely diagnosis of dengue fever is crucial for effective patient management, outbreak control, and implementation of preventive measures.
1. Symptom Management and Treatment:
● Prompt Symptomatic Relief: Early diagnosis allows healthcare providers to offer prompt symptomatic relief, which can alleviate severe discomfort caused by high fever, headache, muscle, and joint pain.
● Avoiding Complications: Early detection is essential for monitoring and managing potential complications, such as dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome, which require immediate medical intervention.
2. Preventing Disease Spread:
● Quarantine and Isolation: Identifying infected individuals early helps in implementing isolation measures to prevent the spread of the virus through mosquito vectors.
● Vector Control Measures: Early diagnosis can trigger targeted vector control measures, such as fumigation and elimination of mosquito breeding sites, to reduce transmission.
3. Epidemiological Surveillance:
● Monitoring Outbreaks: Accurate diagnosis contributes to effective epidemiological surveillance, allowing health authorities to monitor the spread of the disease, identify hotspots, and predict outbreaks.
● Resource Allocation: Surveillance data helps in allocating medical resources and personnel to areas with the highest need, ensuring better preparedness and response.

1. NS1 Antigen:
● NS1 (Non-structural Protein 1) is a protein produced by the dengue virus during the early stages of infection.
● It can be detected in the patient's serum within 1 to 7 days of the onset of symptoms.
● NS1 antigen detection is a rapid and specific diagnostic method, especially useful during the acute phase of the infection.
2. IgM and IgG Antibodies:
● IgM Antibodies: Appear 3 to 5 days after infection, peak around two weeks, and usually disappear within 2 to 3 months.
● IgG Antibodies: Appear 7 to 10 days after infection and can persist for years, indicating past infection or secondary infection.
3. Viral RNA:
● Detected through reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
● Most effective within the first 5 to 7 days of symptom onset, directly confirming the presence of the virus.
NS1 Protein is one of the non-structural proteins of the dengue virus and plays a crucial role in viral replication. The detection of NS1 protein holds significant importance in the diagnosis of dengue:
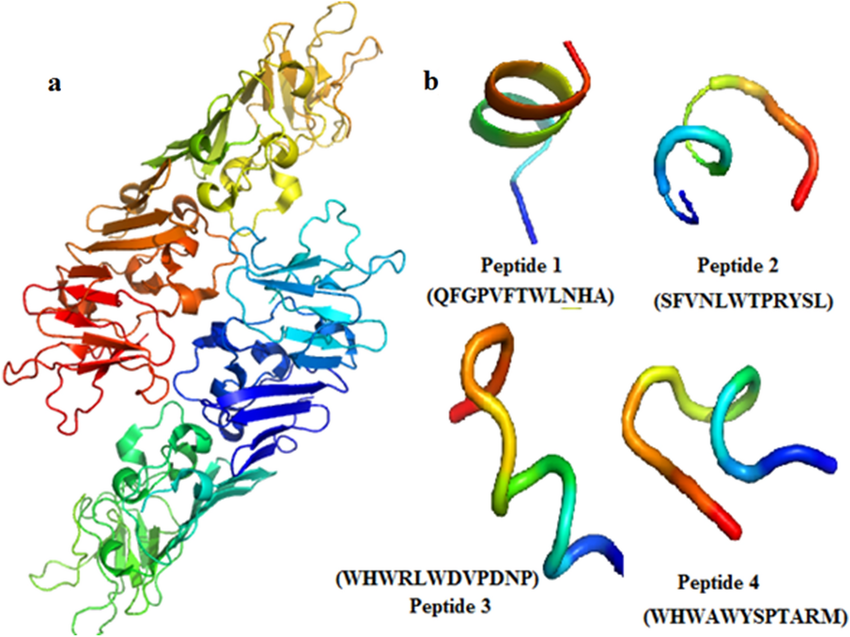
a 3D structure of Dengue virus NS1 protein (PDB ID: 4OIG). b Peptide inhibitors designed against NS1 protein; Peptide 1—QFGPVFTWLNHA; Peptide 2—SFVNLWTPRYSL; Peptide 3—WHWRLWDVPDNP; Peptide 4—WHWAWYSPTARM
1. Early Diagnosis:
● NS1 antigen can be detected in the early stages of the disease, several days before IgM antibodies appear.
● Due to its high expression in the early infection phase, NS1 antigen detection aids in the rapid diagnosis of dengue, particularly within the first 1 to 7 days of symptom onset.
2. High Specificity and Sensitivity:
● NS1 antigen detection offers high specificity and sensitivity, effectively distinguishing dengue virus infection from other flavivirus infections.
● Detection methods include Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) and Immunochromatographic Test (ICT), both of which are quick and accurate.
3. Aid in Clinical Decision-Making:
● Early detection of NS1 antigen allows healthcare providers to confirm the diagnosis promptly, enabling timely and appropriate treatment and management measures to prevent severe complications.
4. Public Health Surveillance:
● NS1 antigen detection assists in epidemiological investigations, monitoring the spread and outbreak of dengue, supporting the formulation and implementation of public health interventions.
5. Combination with Other Detection Methods:
● NS1 antigen detection can be combined with IgM and IgG antibody tests and PCR detection, providing comprehensive diagnostic information and improving diagnostic accuracy.
NS1 antigen, as an early diagnostic marker for dengue, has significant clinical and public health importance. Its high specificity and sensitivity make it a critical tool for the rapid diagnosis of dengue. By combining it with other detection methods, NS1 antigen testing provides comprehensive diagnostic information, supporting timely and effective patient management and disease control measures.
Related Reads
PRODUCT NAME | CAT NO. | Type | Application Platform | Pair Recommendation |
Dengue NS1 | NS1101 | Antibody | LF,CLIA,EIA | Conjugate |
NS1101 | Antibody | LF,CLIA,EIA | Coating | |
NS1101 | Antibody | LF,CLIA,EIA | Coating | |
Streptavidin | SA402 | Antigen | LF | Coating |
Reference
A review on structural genomics approach applied for drug discovery against three vector-borne viral diseases: Dengue, Chikungunya and Zika - Scientific Figure on ResearchGate. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-3D-structure-of-Dengue-virus-NS1-protein-PDB-ID-4OIG-b-Peptide-inhibitors-designed_fig4_359815960 [accessed 22 May, 2024]